ISO 22383:2020 gives guidelines for performance criteria and an evaluation methodology for authentication solutions. We help you to better understand the key points of the standard towards an insight-driven and well-thought-out choice of your authentication system.
Here, we will talk about a new ISO standard dedicated to anti-counterfeiting technologies: the ISO 22383:2020.
It is increasingly necessary for authentication solutions to be more effective in securing supply chain. This both ensures legal trade and creates consumer confidence. The risk of having an abnormal and uncontrolled percentage of counterfeit, falsified and illicitly traded product on the market is increasing due to the development of globalized trade.
In turn, this is boosting the demand for authentication solutions: it is therefore necessary to specify the performance requirements for these solutions along with the features of all impacted processes in the supply chain.
ISO is the International Organization for Standardization, based in Switzerland. It is the world’s largest standard-setting institution, issuing technical standards that cover almost every industry. Its members are the national standards bodies of nearly every country in the world. ISO Standards are sets of rules and criteria internationally agreed by experts. There are a number of ISO Standards aimed at ensuring anti-counterfeiting technologies are fit for purpose. Most are addressed to technology providers. Despite this, ISO 22383:2020 is intended for all organizations needing to validate the authenticity and integrity of material goods with authentication elements and solutions anywhere in the supply chain.
ISO 22383, full name “Security and resilience — Authenticity, integrity and trust for products and documents — Guidelines for the selection and performance evaluation of authentication solutions for material goods” is a revision of ISO 12931. It is aimed to give improved guidelines about the performance criteria and evaluation methodology for authentication solutions used to establish material good authenticity throughout their entire life cycle. It relates to the authenticity of products:
- covered by intellectual property rights
- covered by relevant international, regional or national regulations
- with counterfeiting-related implications
The guideline does not suggest any specific cost–benefit criteria for selecting an authentication solution, but more realistically the cost is one of the main factors to consider. It is universally applicable, irrespective of material goods, environment or authentication technology used and is only one of the guidelines issued by the specific ISO working group on the topic of “Authenticity, integrity and trust for products and documents”.
The guideline helps organizations to identify what type of authentication elements they should use for anticounterfeiting, describing the full lifecycle of authentication solutions: how to choose them (with an evidence and quantitative/qualitative risk assessment approach), how to implement and deploy, and how to operate (measuring their performance).
Strategic analysis for implementing an authentication solution
Any organization needing to implement an authentication solution should start with a preliminary strategic analysis.
The overarching principle for a robust and efficient authentication solutions is to combine diverse elements, incorporating both:
- data-related features such as reliable data capture and retrieval along the product’s life cycle
- authentication elements directly added into the component parts of the product
The factors determining the most suitable authentication elements and solutions are:
- the landscape for implementation, deployment and usage
- an assessment of risks related with counterfeiting
- other logistic, technical and also financial criteria
These factors (fully detailed in the guidan) provide the basis for defining the performance requirements for authentication elements and solutions, and for assessing their effectiveness. The factors should be involved in the following:
- the creation process
- Defining, generating and manufacturing the authentication elements and integrating them with the material goods or its packaging
- the inspection process
- Verifying the authentication elements along the distribution chain by trained people using human senses, tools or references
Some examples of requirements for the strategic analysis may be:
- The organization should not select an authentication solution that affects or alters, in an uncontrolled way, the intended functionality and the integrity of the material goods
- The organization should be aware of applicable laws and regulations especially on privacy and safety
The analysis entails a list of questions to be asked to the right stakeholders, for example:
- What is the likelihood and what are the consequences of the counterfeiting risks on my products, organization and business?
- In which locations are we experiencing counterfeiting and how are the counterfeits being distributed?
- How and by whom will the authentication process be performed?
- What is the impact of human error on the solution (process and authentication)?
Security-by-design concept
It is of the utmost importance that security is not an afterthought at the end of product development.
Security-by-design (ref. §4.2 of the ISO standard) is the concept of adding security into the product, via the implementation of an authentication solution, as early as possible in the product lifecycle.
Categorization of Technologies
The standard identifies three categories of technology (ref. §4.3.5 of the standard):
- Overt
- Covert
- Forensic
Which contain the following characteristics:
- provision of knowledge: the way in which general or good-specific knowledge is provided to the inspector
- sourcing and production of authentication elements and tools: the types of security measures in place to audit providers and protect production processes against knowledge transfer and theft
- inspection: whether inspection is carried out via human senses, an authentication tool or forensic analysis
Performance criteria (based on risk analysis)
The ISO 22383:2020 guideline refers to ISO 31000 for risk management. Nevertheless whichever methodology the organization has decided to follow. It is important to consider the following risk factors:
- risk profile of the material goods
- consequences of counterfeiting
- authentication options
- suppliers (and history) of authentication elements
- counterfeiting history of the material goods
The standard defines some performance criteria helping companies to evaluate how well authentication elements and solutions may perform in relation to the risks identified in the initial strategic analysis.
It also analyzes the issue of what kind of information, related to anti-counterfeiting protection, is disclosed to who (for security and inspection purposes).
The organization is then driven to the choice of the adequate authentication solution through the characterization of both authentication elements and tools and related performance criteria.
The performance criteria can be categorized in the following way:
- ability to provide information feedback or analytical results
- attack resistance
- field/environmental function
- implementation process
- integration process
- physical characteristics
- user friendliness
The main driver is always the risk, however the relative importance of these criteria, their prevalence, can be very variable. This can be highlighted:
- Among the criteria for the selection of authentication elements:
- Physical Characteristics such as dynamicity (robustness and resilience of the element during the production process), durability (under all kind of degradation and aging), health and environmental impact and finally feature-linked characteristics, such as visibility, machine readability, tamper evidence and uniqueness (one-to-one vs. one-to-many)
- Attack Resistance (resistance to tampering and alteration, data breaches, interception of communication and obsolescence)
- Integration Process (how secure the process of integrating the element to the material good is)
- Among the criteria for the selection of authentication solutions:
- Location and environment for the authentication process (availability of power resources, environmental conditions such as temperature or humidity, exposure to hazards, etc.)
- Authentication parameters (the time it takes to process authentication, accuracy rate and speed, the time it takes to get a result, etc.)
- Security policy (the measures that need to be taken to secure all components of the solution, the supply chain, etc.)
- Compliance with relevant regulations (including governmental or those issued by regulatory agencies – especially if the solution is intended for implementation in international markets)
Effectiveness assessment of authentication solutions
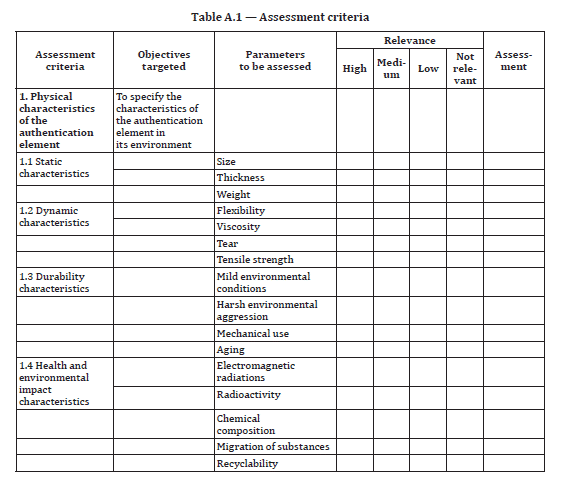
The effectiveness of an authentication element or solution can be assessed by evaluating how well it meets the requirements that have been defined for each set of criteria. ISO 22383:2020 simplifies this assessment by providing a grid in the annex that contains all the performance criteria and allows the user to indicate the performance requirement for each one, as well its relevance.
See below for an extract of this grid
At AlpVision we have made the exercise of measuring the effectiveness of our authentication solutions for some of our typical customers. We can share the results with you on request.
Conclusions
The ISO 22383:2020 standard provides a very solid guideline for implementing authentication solutions. From what we see, the standard focuses on the essentials and does not feature any political bias. It seems therefore as a good starting point for any company being in the process of protecting their products against counterfeiting.
AlpVision’s success is a measure of the effectiveness of the authentication solutions we can propose to a broad range of customers belonging to the most disparate industrial sectors.
This is further confirmed after a thorough analysis performed through the criteria set forth by the new ISO standard ISO 22383.
To keep up to date regarding selection of authentication solutions:
Subscribe to our Newsletter